AMD is set introduce Next-Generation AMD Opteron processors on August 1st, 2006. The Next-Generation AMD Opteron processors were previously known as AMD Opteron revision F CPUs. Following the release of socket AM2 processors the Next-Generation AMD Opteron comes in a new socket -- Socket F. Socket F sports 1,207 pins in a land-grid array similar to Intel’s LGA775 and LGA771 sockets. The new Socket F will be used for dual, quad and eight way processor configurations with up to 16 cores at launch.
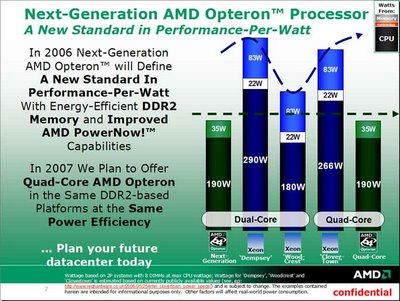
AMD and Intel are both pushing efficiency this year, and AMD is already taking a shot at Intel with its dual and quad-core systems. AMD claims its quad-core Socket F processor, scheduled for launch in 2007, will use the exact same power efficiency as the dual-core processors available today. According to AMD's documentation (right), 90nm 95W dual-core Opterons (scheduled for launch this August) will have the same power draw as 65nm quad-core processors.
Socket F AMD Opteron processors add support for DDR2 and AMD Virtualization. DDR2 with speeds up to 667MHz is supported while the AM2 Athlon 64 X2 and FX chips support DDR2 800MHz. FB-DIMM memory will not initially be supported by Socket F processors. AMD intends to add FB-DIMM support to its processors in the 2008 with the K8L architecture -- nearly two years after Intel launched support. Upcoming revision "G" quad-core processors will also support the Socket F. Previous features such as the integrated memory controller, HyperTransport Technology and AMD64 Execution will continue to be standard features on Socket F processor. With a new socket comes a new naming system too.
This time around AMD has moved to a four digit model number system. Three AMD Opteron families will be available at launch: 1000, 2000 and 8000. 1000 series processors will be Socket AM2 based and replace the existing AMD Opteron 100 series. 2000 series will be Socket F based and aimed towards dual processor systems. 8000 series will be available for four and eight way processor configurations. All three AMD Opteron series will be available as dual-core only. Socket F marks the death of single-core AMD Opteron processors.
Decoding the new model numbers is not too different from the existing system. The addition of a fourth digit simply adds generation designation. The first digit coincides to the series while the second digit coincides with the processor generation. Clock speeds are determined by the last two digits of the model number starting with 10 and increasing in increments of 2. An example of how the new model number works would be the "AMD Opteron 8218" -- which is an eight-way capable processor that’s a second generation Opteron design and clocked at 2.6GHz.
AMD is expected to introduce a full lineup of Socket F processors similar to what it’s done with socket AM2 processors. Socket F processors will be available in models x210, x212, x214, x216, x218 and x220 which are 1.8, 2.0, 2.2, 2.4, 2.6 and 2.8GHz parts, respectively. Regular, HE and SE AMD Opteron models will be available, though clock speeds will vary depending on the Opteron model. Thermal data power for regular AMD Opteron processors will be around 95 watts and 55 watts for AMD Opteron HE processors. Flagship AMD Opteron Model 2220 SE and 8220 SE have a 120 watt TDP while the Socket AM2 AMD Opteron Model 1220 SE has a slightly higher 125 watt TDP. All Opteron processors will have a 1MB of L2 dedicated to each processor core.
Availability is expected July 17th, 2006 under embargo from approved distributors while retail availability is expected August 1st, 2006.

No comments:
Post a Comment